Mastering Reinforcement Learning: A Beginner’s Guide
Author: Manoharan Naidu, Associate Solutions Architect – Applied AI Practice, Searce

What is reinforcement learning and why is it important?
Imagine a machine that learns by trial and error, just like a human! This is the core principle behind Reinforcement Learning (RL), a powerful branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) where agents interact with their environment, receive rewards for good choices, and continuously improve their decision-making.
In recent years, RL has witnessed significant advancements, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. This blog delves into the exciting world of cutting-edge RL research, exploring how Deep Learning is supercharging its capabilities and how researchers are tackling challenges like handling complex actions and limited information. Get ready to discover how RL is transforming various fields, from robotics to self-driving cars, and shaping the future of intelligent systems.
Reinforcement Learning: A Primer
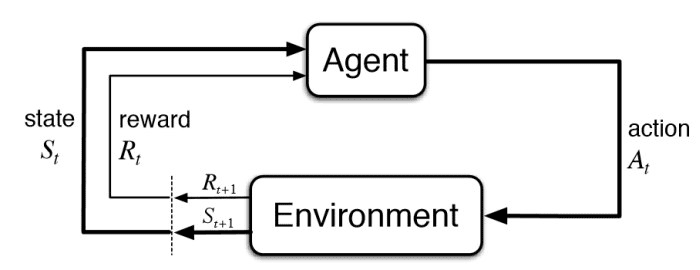
Reinforcement Learning offers a powerful framework for training agents to make optimal decisions in complex environments. At its core, RL operates on a cycle of interaction, reward, and adaptation.
- Agents: These are entities within the RL system, tasked with navigating an environment and achieving a specific goal. In essence, the agent is the “learner” constantly refining its behavior.
- Environment: This represents the external world the agent interacts with. The environment dictates the set of possible states, actions, and the reward structure that guides the agent’s learning.
- State: This refers to a complete snapshot of the environment at a specific point in time. The state serves as the agent’s current understanding of the situation and forms the basis for decision-making.
- Action: These are the choices available to the agent within a given state. The agent selects actions to influence the environment and progress towards its goal.
- Reward: This is the feedback mechanism provided by the environment after an action is taken. Positive rewards signal progress towards the goal, while negative rewards indicate undesirable outcomes. Rewards guide the agent’s learning process by shaping its understanding of what actions are most effective.
Through continuous interaction with the environment, the agent leverages the reward signal to refine its policy, which represents the strategy for selecting actions based on the current state. This iterative process allows the agent to learn optimal behavior without explicit instructions, making RL a valuable tool for tackling problems with dynamic and uncertain environments.
Introducing Deep Reinforcement Learning
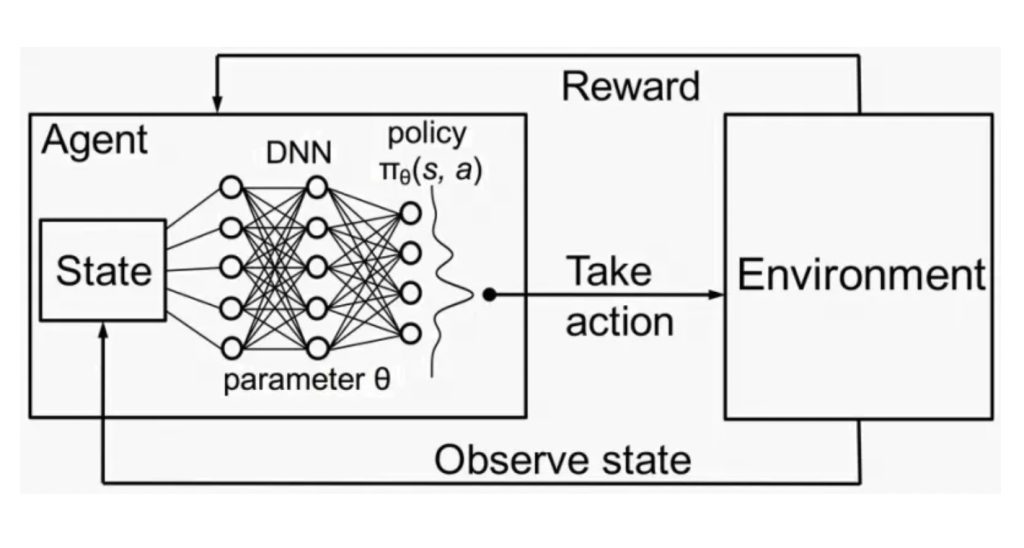
While traditional RL excels in well-defined environments with discrete states and actions, real-world scenarios are often much messier. This is where Deep RL comes in. It injects the power of deep learning into the RL framework, allowing agents to tackle complex tasks with high-dimensional sensory inputs.
Here’s how Deep RL bridges the gap:
Success Stories in Deep RL Algorithms
Several Deep RL algorithms have achieved impressive results in various domains. Here are a few noteworthy examples:
- Deep Q-Networks (DQN): A pioneering algorithm that demonstrated the power of deep learning in RL by achieving superhuman performance on Atari games.
- Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG): This algorithm tackles problems with continuous action spaces, making it suitable for tasks like robot control.
- Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO): Known for its stability and efficiency, PPO is a popular choice for various Deep RL applications.
- Trust Region Policy Optimization (TRPO): TRPO, introduced by OpenAI, addresses the challenge of large policy updates to the model. It acts as a cautious learner, ensuring stability in policy updates. The agent takes smaller, more reliable steps, improving its performance gradually while avoiding drastic changes that could harm its progress.
- Soft Actor-Critic (SAC): SAC, introduced in 2018, improves the agent’s exploration. It is not confined to learning from past experiences and can learn off-policy. It encourages exploration by considering not only the expected reward but also the “entropy” of the policy.
Real-World Applications of Reinforcement Learning?
Reinforcement learning (RL) isn’t just about agents learning to play video games anymore. The ability of RL agents to learn through trial and error, guided by rewards, is making them valuable tools across various industries. Here’s a glimpse into how RL is tackling real-world challenges, incorporating some of the latest advancements, but in no particular order:
- Powering Efficiency: From Data Centers to Power Grids
RL is optimizing various systems behind the scenes. In data centers, it dynamically allocates resources like computing power and storage, maximizing efficiency and minimizing costs. Additionally, RL is being used to optimize power management and distribution in power grids, leading to more efficient and cost-effective energy usage, particularly with the rise of renewable energy sources. - Redefining Traffic Flow: From City Streets to Autonomous Vehicles
The power of RL extends beyond optimizing data centers. Traffic control systems are also benefiting from RL algorithms that can help optimize traffic signals in real-time, reducing congestion and improving traffic flow. This not only aids in urban mobility but also reduces the environmental impact of traffic. Speaking of autonomous vehicles, RL is crucial in their development, enabling them to learn from their environment and make safe, efficient driving decisions. Companies like Waymo and Tesla are leading the way in autonomous vehicle technology with the help of this technology. - The Future of Finance: From Algorithmic Trading to Personalized Recommendations
The financial sector is another area embracing RL. Here, RL plays a crucial role in portfolio management and algorithmic trading, optimizing strategies to maximize returns and minimize risk. For instance, JPMorgan’s LOXM trading algorithm leverages RL to execute trades at the best prices and maximum speed. Interestingly, RL algorithms are also being used to personalize recommendation systems, like those used by Netflix and Amazon. By analyzing your past interactions, RL can suggest content or products that you’re most likely to enjoy, improving user engagement and satisfaction. - Revolutionizing Healthcare: From Chronic Disease Management to Personalized Treatment
The potential of RL extends to the healthcare field as well. Here, RL offers the potential for personalized treatment plans based on individual patient data, potentially improving patient outcomes in chronic disease management. - Optimizing Supply Chains: From Manufacturing to Retail
Industries with intricate supply chains, like manufacturing and retail, are finding RL particularly beneficial. RL can optimize logistics and inventory management, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency. - Mastering Languages: From Machine Translation to Natural Language Processing
Advancements in RL are improving various Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. By allowing models to learn from feedback and adjust their strategies, RL is leading to more accurate and nuanced language models, with improvements in machine translation, sentiment analysis, and other NLP tasks. - Conquering Games: From Pixels to Champions
Reinforcement learning has revolutionized the gaming industry. It has paved the way for the development of AI that can master complex games and often outperform humans. For example, Google’s DeepMind trained its AI AlphaGo to not just play the game of Go but also—with the help of reinforcement learning—defeat two world champions of Go, Lee Sedol and Ke Jie, in 2016 and 2017, respectively. - Transforming Robotics: From Assembly Lines to Disaster Zones
Imagine robots that can navigate complex environments and perform intricate tasks with human-like dexterity. RL is making this a reality. By interacting with their surroundings and receiving rewards for successful actions, robots equipped with RL can learn to perform tasks like:- Assembly Line Automation: Robots can learn to precisely manipulate objects on assembly lines, adapting to variations and improving efficiency.
- Warehouse Management: RL-powered robots can navigate warehouses, autonomously picking and placing items, optimizing storage and retrieval processes.
- Search and Rescue: Robots equipped with RL can navigate disaster zones, locate survivors, and even provide basic medical aid.
These are just a few examples of how RL is transforming various domains. As research progresses, we can expect even more innovative applications. The potential of RL to tackle complex problems and automate tasks makes it a key player in shaping the future of artificial intelligence.
Conclusion
Reinforcement learning (RL) has graduated from the realm of science fiction to a powerful tool transforming real-world applications. Its ability for agents to learn through trial and error, guided by rewards, is making significant waves across various industries. From optimizing data centers and power grids to revolutionizing robotics and healthcare, RL is shaping the future of intelligent systems.
As research in Deep RL continues to evolve, we can expect even more groundbreaking advancements. The potential for RL to tackle complex problems, automate tasks, and improve decision-making across various domains is truly exciting. This technology holds the promise of a more efficient, optimized, and intelligent future.
Are you ready to explore the exciting world of RL? Join the conversation and be part of shaping the future of AI with reinforcement learning!